Table of Contents
In the first part of our blog series on the subject of industrial gas, we described the inspection of the entire gas system and the latest technical options.
In this blog, the identified defects found in the industrial plant are now presented and explained in a helpful way. But first a few basic remarks.
Of course, gas pipeline systems must be designed in a way that they remain technically tight and resist the expected loads. Most of these can be limited to mechanical, chemical and thermal nature.
When can we describe a plant as “technically tight”? In most cases, it can be assumed that a leak test has been carried out successfully using the procedure in the German DVGW worksheet G 600 (TRGI). Decades of practice have shown that leaks can still occur over the long service life of an industrials gas system.
Leaks
Leaks are found relatively often in the extensive pipeline systems on industrial sites and they can be tracked back to various causes. In the case of leaking fittings, it is usually the unavoidable aging process, the lack of operation and maintenance, whereas in the case of leaky threaded connections, the use of hardening sealant can be observed.
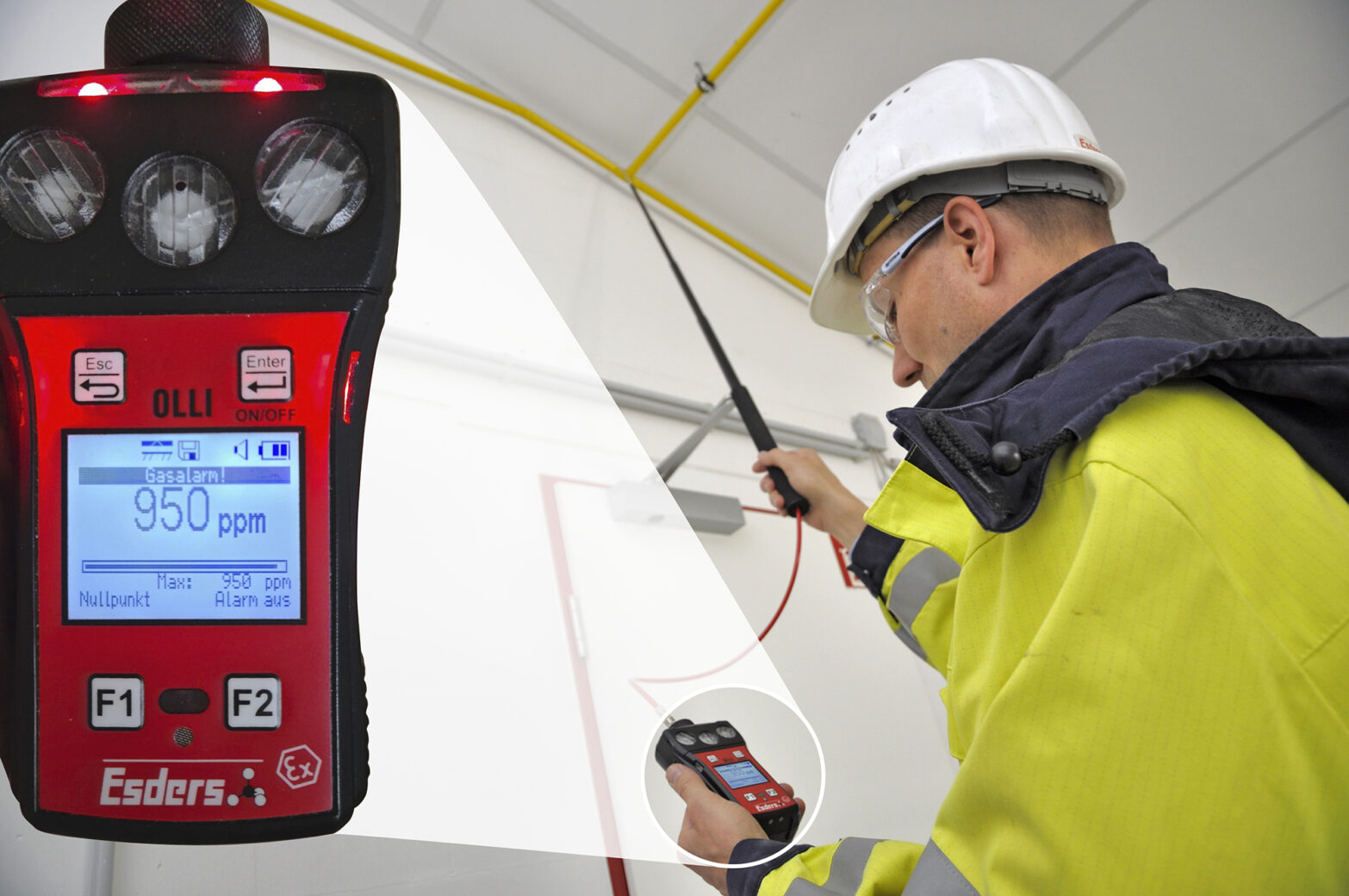

Since the gas pipees are often laid 2 to 3 meters away, the inspector on site needs a probe with a telescopic rod in order to be able to work efficiently. Almost 70% of pipes can be inspected in this way. In around 20% of the applications, a mobile working platform has to be provided by the client. The rest can usually be reached normally by walking along the pipe system. A pipe section at a height of 25 meters could only be inspected by using a mobile crane.
Assessing the possible risk of leaks is different from a gas house installation, due to the line routing, usually as an exposed indoor or outdoor pipe, . Taking a reduced risk potential into account, it is possible for the specialist to classify identified leaks and to classify them into a leak class. This offers a decision-making aid about the type and sequence of damage removal. When making a decision, the person carrying out the work should use the table below, which was taken from DVGW worksheet G 614-2.
Classification and Evaluation Scheme for Leaks
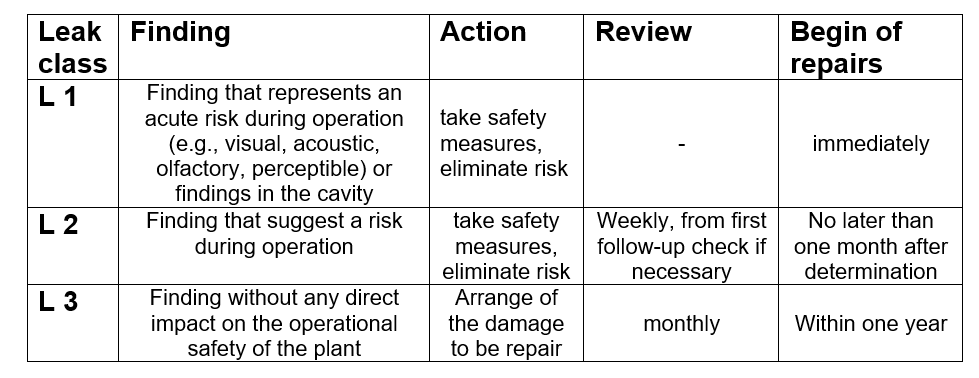
The decisive criterion for assigning the leakage to leak classes L 1, L 2 or L 3 is the measured natural gas concentration in the environment of the leak. For this purpose, measurements are taken all the way around at a distance of 10 centimeters and the highest concentration found at the leak point was used. Of course, the measurement technology used also plays a decisive role here, as the readings of measurement devices with diffusion measuring heads differ significantly from those of pump devices.
You can read about the exact differences in how a measuring device works with and without a pump in our blog post Gas readings – differences between diffusion and pump devices.
As one can imagine, other deficiencies are also found in a widely ramified pipeline system which, has been constantly expanded over decades and has been exposed to the forces of nature.
Corrosion Protection
In particular, freely laid pipelines must be protected against corrosion in a suitable manner, insofar as they are not corrosion-resistant. Special corrosion protection measures are normally also required in the area where the pipeline supports the fastening. The protective coating applied to prevent corrosion is often only partially present.
Pipe supports
Pipe supports are an essential part of a gas pipeline system. In the case of exposed external pipes in particular, they must be arranged in such a way that the gas pipe can move in a defined manner without inadmissible forces being exerted in the supporting structure. This permanently prevents damage to the pipe or the pipe casing.

Color Coding and Flow Direction Labelling
Often there are pipes on pipe bridges with a “uniform” protective coating provided that transport different media. In the case of trouble, the emergency services are faced with an almost impossible task when it comes to media allocation or blocking or securing of an affected line section. For this reason, freely laid natural gas pipelines should consistently be painted yellow and, if possible, with the signs “MP” (medium pressure) and LP (low pressure) as well as other flow direction markings in accordance with the operating pressure.
Mechanical Stress
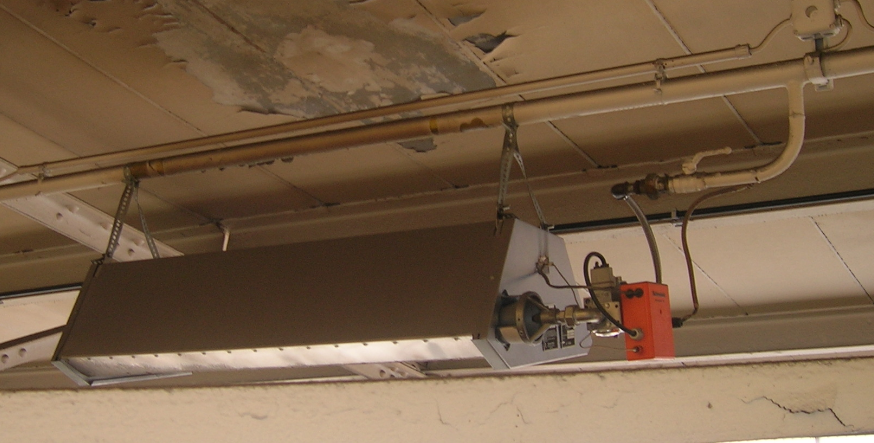

For various reasons, a circuit system is often used as a fastening element. Fastening lamps and gas emitters to the gas pipe represents an impermissible mechanical load and is therefore prohibited.
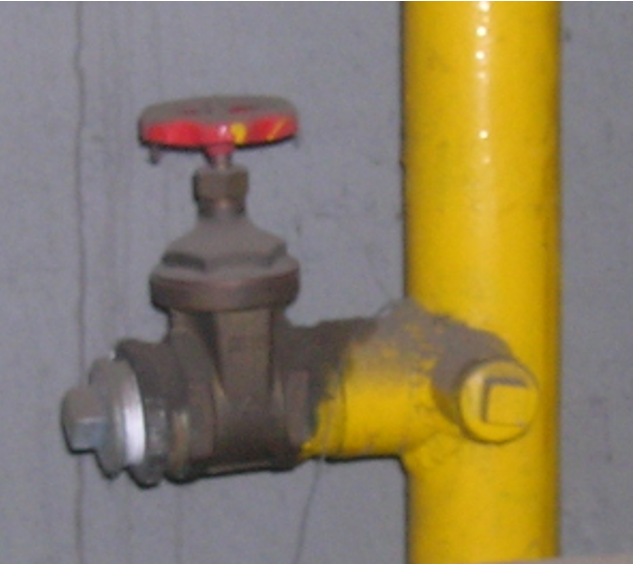
Wrong Materials
Components and fittings for use in drinking water installations, as shown in the picture, are of course neither tested nor approved for operation with natural gas.

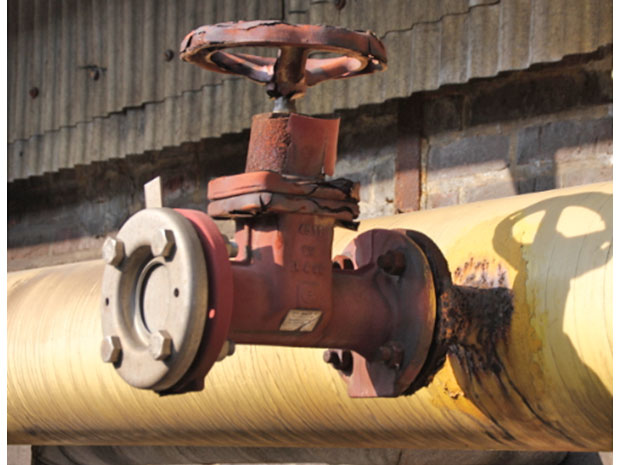
Unsealed Pipe Ends
In industrial companies in particular, changes and shutdowns of pipeline sections are the agenda for production-related reasons. Completed gas pipes are usually secured, as the work is carried out by approved specialist companies. At this point I would also like to say a word about inoperative gas pipes, that means gas pipes to which no gas appliance is connected. Technically correct, they are designated as unused pipes. These should be disconnected and retained at the branch of the gas-carrying pipe.

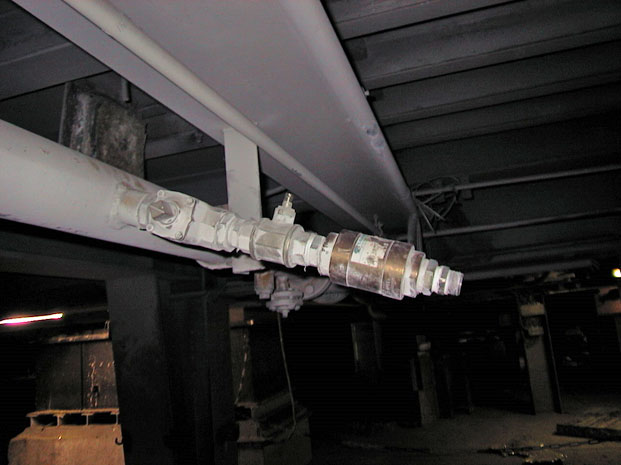
Lightning Protection
Often the required lightning protection of the pipe system is not clearly recognizable for the “gas man”. In general, exposed external pipes are to be included in a lightning protection concept. A relevant specialist company should always be commissioned to carry out the work.
Potential Equalization
The statements on the subject of lightning protection can also be transferred to the subject of potential equalization 1:1. Gas pipes must not serve as arresters or earth electrode in lightning protection systems and neither be used or shared as protective and operational earth electrodes nor as a protective conductor in electrical systems. The metallic inner pipes of each building have to be connected to the respective potential equalization. This inspection should also be carried out by a specialist company.
Defect Classes
As mentioned at the beginning of this blog, it is important to classify any deficiencies that have been identified, taking into account the risk potential. The ranking into defect classes offers support on the decision about the type and sequence of damage repair. This is a great advantage, because, due to the large number of individual defects, it is often not possible to repair the defect immediately, but it is also not absolutely necessary.

Unsecured pipe openings e.g., have to be stored immediately and properly, whereas the corrosion damage to an exposed external pipe can be treated as part of a maintenance plan.
In accordance with the classification carried out by the specialist, measures can be initiated which include the defense against a possible risk as well as repair or replacement.
The following classification and evaluation scheme for defects provides good assistance.
Classification and Evaluation Scheme for Defects
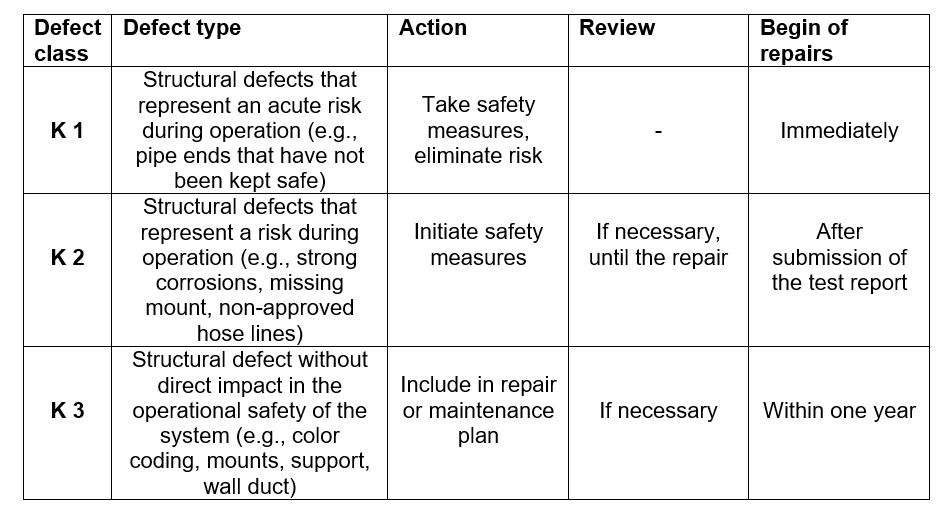
While the classification and evaluation scheme for leaks offers little scope for interpretation, here the readings and their measures are clearly defined, the implementation of the classification and evaluation scheme for defects depends largely on the expert’s wealth of experience. A clearly readable gas concentration in the ppm range can be assigned more easily than structure defects and whether these represent an acute risk or just a risk. Here boundaries are certainly very individual and fluid. In case of doubt, the next higher defect class should always be selected or a joint assessment of the restoration and the start of the repair should be agreed with in writing with the operator. It is significant to add that any additional checks and the start of repairs depend on the classification. For the operator it plays a decisive role whether a measure has to be carried out immediately or within a year.
Summary of the defects
As every reader can surely understand, after many years of operation, a not inconsiderable number of defects are found in a pipe network inspection. In addition to the operating time, there is also a pipe length of several kilometers. The classified leaks and defects must then be prepared for the system operator. For this purpose, tables in Excel can be used, which can be evaluated and filtered as required.
A photographic recording of the defects has also proven itself. The picture of a leaking pipe is certainly not very meaningful for the matter of the defect, but it can serve to localize the defect and it can be extremely helpful in later elimination periods. Here the picture number should also correspond to the number of the defect that was recorded in the table.
In the next blog post in our industrial gas series, the topic of rempairing defects, information on the organisational structures of an industrial company and future inspection intervals will be dealt with.

